Ùmap leads in digital mapping, transforming how we analyze and visualize geographic data for better urban planning, emergency responses, and global insights.
In today’s digital era, mapping technology has evolved significantly, revolutionizing how we perceive and interact with geographic data. From traditional paper maps to sophisticated digital platforms, Ùmap stands at the forefront of this transformation, offering versatile solutions that cater to diverse user needs.
Evolution of Mapping: From Paper Maps to Digital Platforms

Mapping has undergone a remarkable evolution, transitioning from manual cartography on paper to advanced digital platforms like Ùmap. Initially reliant on physical surveys and hand-drawn maps, the advent of computers and Geographic Information Systems (GIS) revolutionized the accuracy, accessibility, and scope of mapping technologies.
GIS enabled the integration of spatial data with attributes and metadata, facilitating complex analyses and visualizations that were previously unimaginable.
This evolution paved the way for the development of digital maps that are dynamic, interactive, and capable of real-time updates, fundamentally changing how individuals, businesses, and governments interact with spatial information.
The Rise of Versatile Mapping Technologies:
Modern mapping technologies, exemplified by Ùmap, have democratized access to spatial information. These platforms integrate real-time data, satellite imagery, and sophisticated algorithms to offer dynamic maps that facilitate navigation, urban planning, disaster management, and more.
Ùmap, in particular, excels in its ability to aggregate diverse datasets seamlessly, providing users with comprehensive views of geographic features, infrastructure, and environmental conditions.
Whether used for exploring terrain, monitoring weather patterns, or analyzing demographic trends, Ùmap empowers users to make informed decisions based on accurate spatial insights.
Types of ùmap:
Geographic Information Systems (GIS):
Ùmap leverages Geographic Information Systems (GIS) to organize, analyze, and visualize spatial data. GIS allows users to overlay different layers of information, perform complex queries, and derive insights crucial for decision-making across various sectors.
From environmental assessments to urban planning and disaster response, GIS-powered Ùmap applications play a vital role in optimizing resource allocation, mitigating risks, and enhancing operational efficiencies.
Virtual and Augmented Reality Maps:
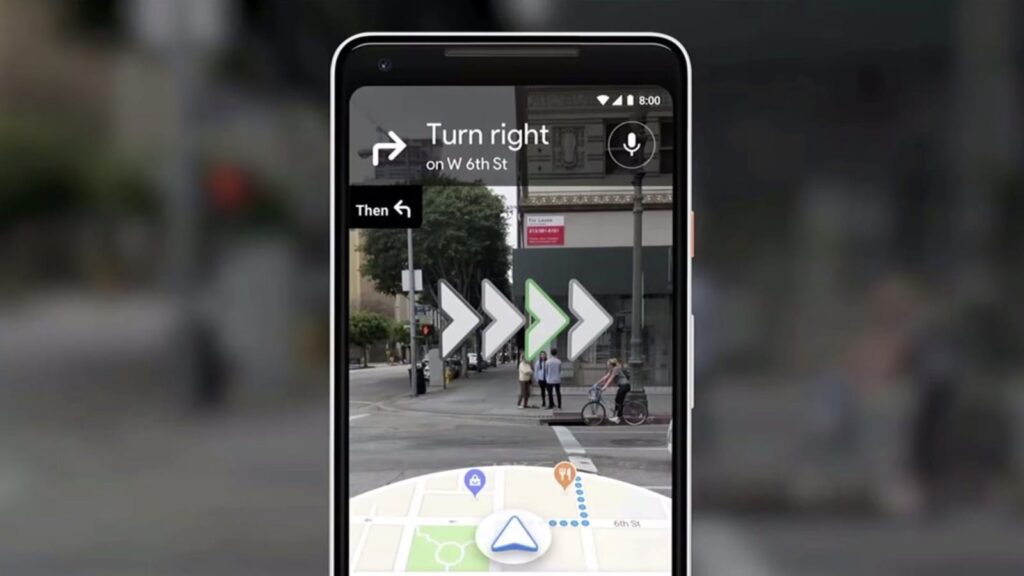
Ùmap incorporates Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) technologies to provide immersive mapping experiences. VR enhances spatial perception by allowing users to navigate simulated environments, making it valuable for training, simulations, and virtual tours.
AR overlays digital information onto the real world, enabling users to access contextual data in real-time through mobile devices or specialized eyewear. These technologies expand the utility of Ùmap beyond traditional mapping, offering innovative ways to interact with spatial information and visualize complex datasets.
Interactive Web ùmaps:
Interactive web ùmaps offer users seamless navigation, real-time updates, and collaborative features. These maps, accessible via browsers and mobile devices, empower users to explore geographic data, share information, and contribute to crowdsourced mapping efforts.
Ùmap’s interactive capabilities facilitate community engagement, support public participation in planning processes, and enable stakeholders to collaborate on spatial projects effectively. By fostering open access to geographic information, Ùmap promotes transparency, accountability, and informed decision-making in diverse contexts.
Advantages of Using ùmap:
Ùmap offers numerous advantages, including enhanced spatial visualization, accurate location-based services, and improved decision-making capabilities. Its user-friendly interfaces and customizable features make it accessible to a wide range of users, from casual consumers to professionals in diverse industries.
By integrating data from multiple sources into cohesive visualizations, Ùmap enables stakeholders to gain comprehensive insights into spatial relationships, patterns, and trends.
This capability is invaluable for optimizing workflows, identifying opportunities, and addressing challenges in sectors such as transportation planning, natural resource management, and public health.
Also read: Oh Em Gee Blog – Discover Exciting Travel Destinations and Tips!
Applications in Various Industries:
Ùmap finds applications across multiple industries, including urban planning, transportation, agriculture, environmental management, and emergency response. By providing tools for spatial analysis, scenario modeling, and predictive mapping, Ùmap supports evidence-based decision-making and strategic planning.In urban planning, for instance, Ùmap helps stakeholders visualize proposed developments, assess their impact on infrastructure, and engage with community stakeholders effectively.
Similarly, in agriculture, Ùmap facilitates precision farming practices by mapping soil conditions, monitoring crop health, and optimizing irrigation strategies based on localized data. These applications demonstrate Ùmap’s versatility and its ability to drive innovation across sectors by harnessing the power of spatial intelligence.
Challenges and Limitations:
Despite its benefits, Ùmap faces challenges such as data accuracy issues, privacy concerns related to location data, and the need for continuous updates to maintain relevance. Addressing these challenges requires collaboration between stakeholders and ongoing advancements in technology.
Ensuring data integrity and protecting user privacy are paramount concerns, particularly as Ùmap expands its capabilities to include real-time tracking and personalized services. Additionally, maintaining interoperability with existing systems and adapting to evolving regulatory frameworks present ongoing challenges for developers and users alike.
Overcoming these hurdles requires a proactive approach to data governance, cybersecurity, and stakeholder engagement to build trust and ensure the responsible use of spatial information.
Future Developments and Innovations:

The future of Ùmap promises exciting developments, including enhanced AI-driven analytics, greater integration with IoT devices, and advancements in 3D mapping technologies. These innovations are poised to further expand Ùmap’s capabilities and applications in the digital age.
AI algorithms will enable Ùmap to analyze complex datasets more efficiently, extracting actionable insights and predictive analytics that enhance decision-making in real-time. Integration with IoT devices, such as sensors and drones, will enable Ùmap to capture dynamic data streams and monitor changes in real-world environments continuously.
Meanwhile, advancements in 3D mapping technologies will enhance the realism and immersion of virtual environments, making Ùmap indispensable for applications ranging from urban design simulations to virtual tourism experiences.
By embracing these innovations, Ùmap is positioned to lead the next wave of digital transformation, offering users unprecedented tools to explore, understand, and interact with the world around them.
FAQs:
1. What does Ùmap stand for?
Ùmap stands for “Ubiquitous Map,” symbolizing its widespread accessibility across digital platforms.
2. What can users do with Ùmap?
Users can utilize Ùmap for navigation, spatial analysis, urban planning, disaster management, environmental monitoring, and more.
3. How is Ùmap revolutionizing the digital age?
Ùmap democratizes access to spatial information, enhances decision-making across industries, and fosters innovation in geographic data visualization and analysis.
4. What are the advantages of using Ùmap?
Advantages include enhanced spatial visualization, accurate location-based services, and improved decision-making capabilities across diverse industries.
5. In which industries does Ùmap find applications?
Ùmap is applied in urban planning, transportation, agriculture, environmental management, emergency response, and other sectors for spatial analysis and strategic planning.
Conclusion:
Ùmap represents a cutting-edge leap in mapping technology, offering powerful tools for visualizing and analyzing geographic data with precision. Its ongoing evolution promises to reshape how we navigate and understand our world, empowering better urban planning, emergency responses, and global insights.
Related Post:



